Asunercept – Overview
Apogenix’ lead drug candidate asunercept is a fully human fusion protein that consists of the extracellular domain of the CD95 receptor and the Fc domain of an IgG antibody. Asunercept is being developed for the treatment of solid tumors, malignant hematological diseases, and viral infections, and has been evaluated in the treatment of glioblastoma, myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), as well as COVID-19.
The excellent tolerability of asunercept was shown in a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase I trial in healthy volunteers. Even the highest dose of 20 mg/kg body weight was very well tolerated and no anti-drug antibodies against asunercept were detected.
Asunercept as a Therapeutic for Solid Tumors
Asunercept inhibits the CD95 ligand which plays an important role in the progression of solid tumors. Depending on the target cell – immune cell or tumor cell – the interaction between the CD95 ligand and the CD95 receptor induces either apoptotic cell death or invasive growth of cells. Consequently, asunercept has a dual mechanism of action.

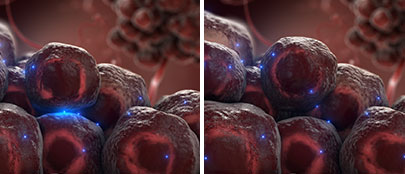
Inhibition of Tumor Immune Escape
(Immune Cells):
The interaction between the CD95 ligand on tumor endothelial cells and on tumor cells and the CD95 receptor on immune cells leads to the death of apoptosis-sensitive immune cells before they can enter the tumor in order to attack it. This process is called tumor immune escape.
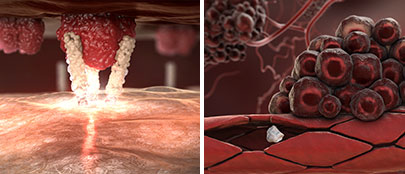
Asunercept blocks the CD95 ligand on tumor endothelial cells and on tumor cells, thereby preventing its interaction with the CD95 receptor on immune cells. As a result, immune cells remain intact and can enter the tumor in order to attack it.
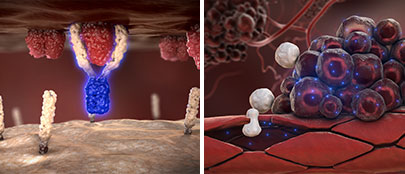
Inhibition of Invasive Growth
(Tumor Cells):
The second mechanism by which the CD95 system promotes the growth of solid tumors is the binding of the CD95 ligand to the CD95 receptor on tumor cells. This interaction activates an intracellular signaling pathway that stimulates the invasive growth of tumor cells.
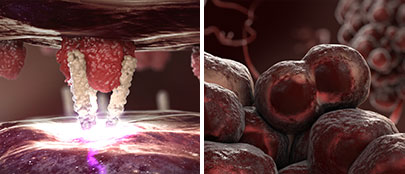
By blocking the CD95 ligand, asunercept prevents the CD95 receptor from binding to its ligand. As a result, the invasive growth of tumor cells is inhibited.
Asunercept for the Treatment of Glioblastoma
In a randomized, controlled phase II efficacy trial in recurrent glioblastoma, treatment with asunercept in combination with radiotherapy has shown statistically significant improvements in progression-free survival at six months, median progression-free survival, and quality of life, as well as a positive trend in overall survival compared to treatment with radiotherapy alone.
Role of Biomarkers
Glioblastoma patients having a newly-identified biomarker associated with the CD95 ligand – the target of asunercept – experienced the greatest benefit from treatment with asunercept. The trial showed a significant increase in median overall survival in biomarker-positive patients treated with asunercept.
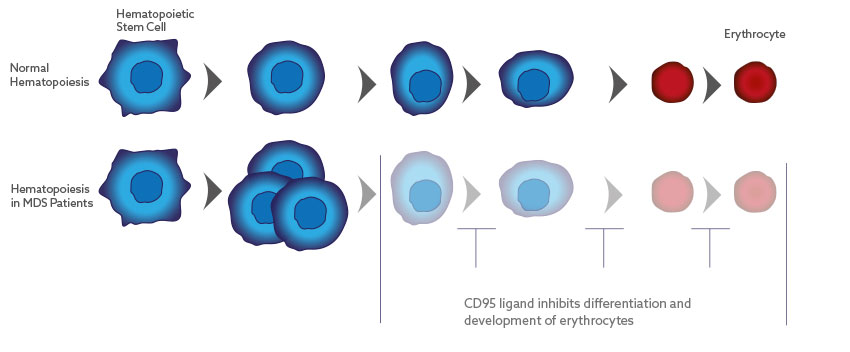
Asunercept for the Treatment of Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
In MDS, the CD95 ligand inhibits the differentiation and development of red blood cells. Asunercept blocks the CD95 ligand, thereby enabling the maturation of erythrocyte precursor cells to functional erythrocytes. Preclinical studies with bone marrow from MDS patients show that asunercept dose-dependently stimulates erythropoiesis.
Final results from a phase I trial with asunercept in low and intermediate-1 risk MDS patients demonstrated the tolerability as well as activity of the drug candidate - the substance stimulated erythropoiesis and led to a clear decrease in transfusion frequency in this patient population. Apogenix is currently in preparation of phase II proof-of-concept trials to further evaluate the efficacy and safety of asunercept in the treatment of MDS.
Asunercept for the Treatment of COVID-19
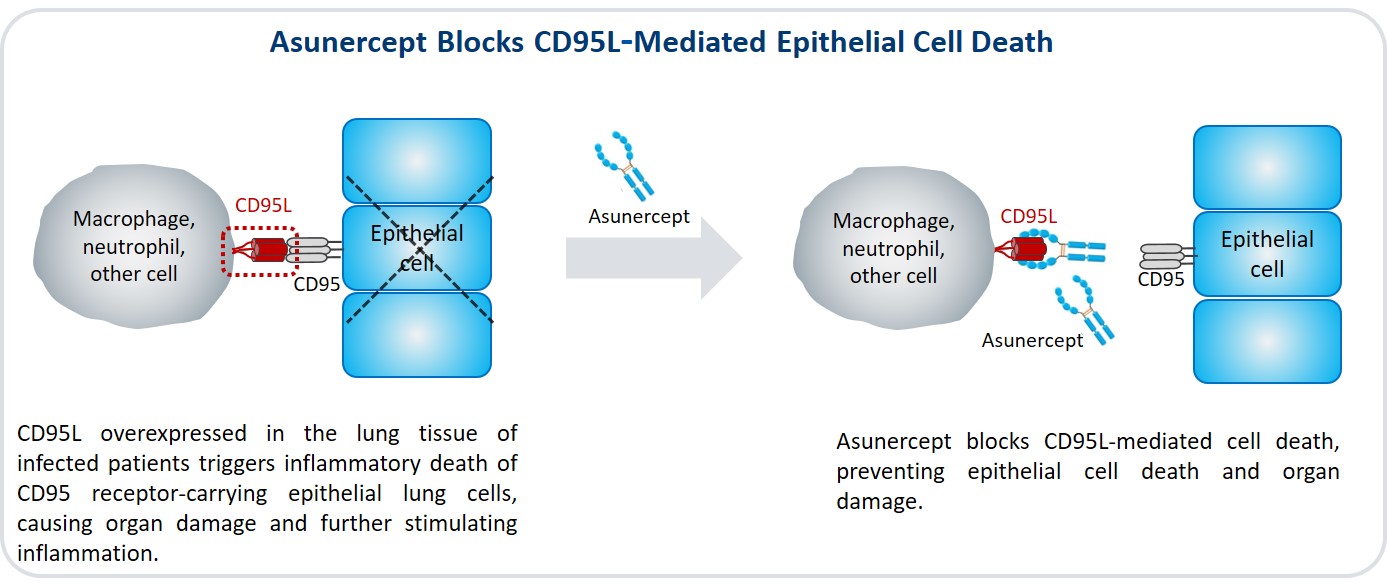
Throughout disease progression of viral infections such as COVID-19, CD95L causes severe dysregulation of the immune system. This results in two major pathological problems – reduced lymphocyte counts (lymphopenia) and inflammatory cell death, leading to pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), respectively.
Published data show that CD95 levels are increased in the lung of ARDS patients and cause the inflammatory death of epithelial cells. The addition of CD95L inhibitors prevents epithelial cell death in ARDS and thereby offers new therapeutic options for ARDS.
Newly published evidence indicates that CD95L plays a role in the induction of life-threatening lymphopenia and inflammatory cell death in COVID-19 patients. Studies in Chinese COVID-19 patients consistently report that the severity of lymphopenia correlates with the severity and the outcome of the disease.
By blocking CD95L, asunercept could reduce CD95L-mediated lymphopenia and the excess of inflammatory cell death reported in ARDS patients. By directly targeting two critical pathogenic mechanisms, asunercept could therefore represent a unique therapeutic approach for viral infections such as COVID-19.